Introduction:
NVMe over TCP (NVMe/TCP) is becoming increasingly popular as it delivers high performance and scalability over standard Ethernet networks. When deployed with VMware ESXi and Hitachi VSP One Block 20 Series storage, it can support critical workloads efficiently.
However, in ESXi 8.0U3f and earlier builds, default configurations may lead to performance delays. Additionally, presenting many namespaces across multiple subsystems can result in excessive NVMe controllers, straining ESXi resources during outage recovery.
This blog explains and highlights the issues, root causes, and best practice recommendations to optimize NVMe/TCP with Hitachi storage.
Performance Observations on ESXi Hosts:
In ESXi 8.0U3f and earlier builds, certain operations may exhibit slower performance and resource consumption on the ESXi host. These operations include:
- Virtual machine creation may take longer
- Datastore creation can experience delays
- Disk allocation within VMs may be slower than expected
- Excessive NVMe/TCP subsystems on the ESXi host can lead to high resource consumption during error recovery
- Multiple controller failures from a single target port outage can degrade ESXi host stability and hinder full recovery
Root Cause Analysis:
Analysis 1: Latency Issue
- Hitachi VSP can send read data to ESXi hosts within ~1 millisecond.
- VMware ESXi delays the acknowledgment (ACK) by a few milliseconds.
- Since read completion is tied to ACK → CQE, overall latency increases.
- This behaviour resembles a “delayed ACK” but is not officially supported for NVMe/TCP, leading to performance degradation.
Analysis 2: Resource Exhaustion
- A single target port failure can cause many NVMe/TCP controllers on the ESXi host to go offline at once.
- Mass recovery attempts can overload ESXi system resources, preventing full recovery of some controllers. For details, this site can be referred from Broadcom: Recommendation for ESXi NVMe/TCP Configuration for Hitachi Storage Array
Understanding Submission Queue (SQ) Flow Control:
In NVMe architecture, hosts communicate with storage devices through Submission Queues (SQs) and Completion Queues (CQs). SQ Flow Control ensures commands are completed in an orderly manner.
- With SQ Flow Control enabled: The storage system waits for the host to send an acknowledgment (ACK) before considering a read operation complete. This means every read is dependent on the host’s response time.
- When SQ Flow Control is disabled: The storage system can finalize the read operation immediately after sending the data (C2HData) without waiting for an explicit ACK from the host. This may reduce latency and speeds up overall performance.
Best Practices:
Practice 1: Disable SQ Flow Control
> Hitachi recommends disabling SQ Flow Control by upgrading to ESXi 8.0U3g (build 24859861) or later, where the performance delay has been addressed. With SQ Flow Control disabled, Hitachi VSP storage can use Auto RSP to finalize reads without waiting for the ESXi host’s delayed acknowledgment.
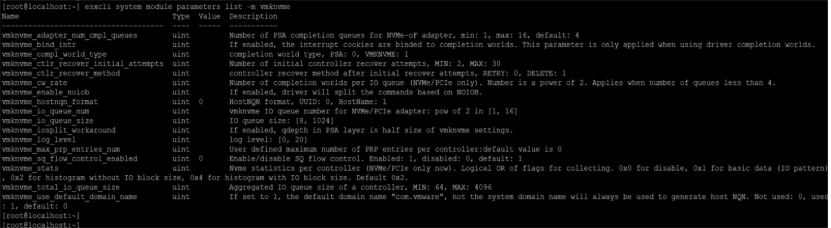
> Run the following command to disable SQ Flow Control: # esxcli system module parameters set -m vmknvme -p "vmknvme_sq_flow_control_enabled=0"

> Preserve other existing parameters when applying:
# esxcli system module parameters set -m <module name> -p "<p1>=<v1> <p2>=<v2> <p3>=<v3>... <pn>=<vn>"
Here, we have applied the following command to keep both the ‘vmknvme_hostnqn_format’ and ‘vmknvme_disable_sq_flow_control’ disabled

> Verify the Configuration
> Reboot the ESXi host for the new configuration to take effect.
#date; reboot

Practice 2: Limit NVMe Subsystems per ESXi Host
- Export multiple namespaces through fewer subsystems to minimize controller count.
- VMware recommends limiting ESXi connections to a maximum of 8 subsystems per host.
- This avoids resource exhaustion and controller recovery issues during outages.
For more details, please refer to the Broadcom site: Recommendation for ESXi NVMe/TCP Configuration for Hitachi Storage Array
Benefits of Disabling SQ Flow Control and Limit Subsystems per ESXi Host
- Significant latency reduction — Read completions occur at ~1ms instead of 100ms.
- Faster VM provisioning — Virtual machines can be created quickly without delay.
- Smoother datastore operations — Datastore creation and expansion run efficiently.
- Improved workload performance — Disk allocations within VMs are faster, improving user experience.
- Prevents resource exhaustion – avoids overwhelming ESXi during error recovery.
Conclusion
NVMe/TCP provides high performance for VMware environments, but tuning is essential. Disabling SQ Flow Control reduces latency and eliminates ACK-related delays, while limiting subsystems per host prevents resource exhaustion and improves stability during outages. With these best practices on Hitachi VSP One Block 20 Series storage and ESXi 8.0U3g or later, organizations can achieve consistent low latency, reliable recovery, and scalable performance.