Introduction
Managing distributed cloud environments on bare-metal infrastructure can be challenging, especially when integrating enterprise storage for stateful workloads.
The setup consists of Google Distributed Cloud (software only) on Bare-Metal where Cassandra statefulset is running with persistent volume from Hitachi VSP storage systems. The volumes from VSP storage systems are provisioned by CSI Driver HSPC (v3.16.1).
In this blog, we walk through the process of deploying Google Distributed Cloud (software only) on Bare-Metal and creating a StatefulSet (running Cassandra) with volumes provisioned by CSI Driver HSPC (v3.16.1). Upgrade the GDC cluster from v1.31 to v1.32 and verify that the StatefulSet is still running and has no downtime during the upgrade.
Overall objective was to ensure stable, persistent storage for Cassandra throughout the upgrade process. The upgrade proved seamless, the HSPC plugin v3.161 delivered reliable storage and the StatefulSet remained healthy after the cluster upgrade, demonstrating the robustness of the solution.
Key Elements and Functions
Google Distributed Cloud (software only) for bare metal:
GDC (software only) is a cloud-centric container platform that provides you with a consistent platform to construct and manage modern hybrid and multi-cloud environments through a single pane of glass with Google Cloud console. GDC (software only) runs on-premises in a bare metal environment. GDC on bare metal is software that brings Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) to on-premises data centers.
GDC unifies the management of infrastructure and applications across on-premises, edge, and in multiple public clouds with a Google Cloud-backed control plane for consistent operation at scale.
HSPC: A CSI plugin from Hitachi used to provision persistent volume from the Hitachi storage system to Red Hat OpenShift or Kubernetes cluster to preserve and maintain data after the container life cycle ends.
Hitachi Storage Plug-in for Containers (HSPC) provides connectivity between Kubernetes containers and Hitachi Virtual Storage Platform (VSP) storage systems.
Integration between GDC on-prem and VSP series storage using Container Storage Interface (CSI) means users can consume enterprise-class storage by abstracting the complexity of the underlying storage infrastructure.
Hitachi CSI plugin HSPC is GDC Ready storage qualified. Refer the following URL for validated versions.
https://docs.cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/enterprise/docs/resources/partner-storage#hitachivantara
Hitachi VSP: A VSP storage system was used for persistent volume in GDC deployed on on-premises.
Testbed Configuration
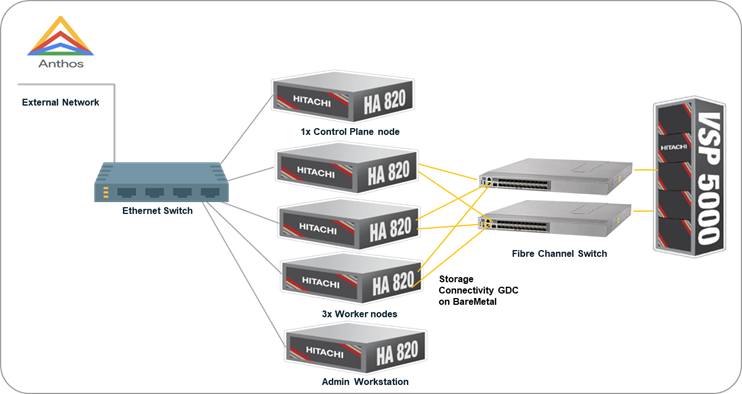
Resources used in this environment
Hardware:
|
Item
|
Descriptions
|
|
Hitachi Advanced Server HA820 G2
|
5x Bare Metal servers (1x Control Plane, 3x Worker nodes and 1x Admin Workstation).
|
|
Hitachi VSP 5600
|
Hitachi VSP 5000 Storage System serving as Block storage for persistent volume to the cluster.
2x 32G FC Ports were used.
|
|
Brocade and Cisco MDS Switch
|
Fibre Channel (FC) Switches providing SAN connectivity to the datacenter storage network.
|
|
Ethernet Switch
|
Cisco Network switch at the data center to provide Management network connectivity between resources.
|
Software:
|
Item
|
Descriptions
|
|
Google Distributed Cloud (Software Only)
|
v1.31 and v1.32
|
|
HSPC
|
Hitachi Storage Plug-in for Containers (v3.16.1) CSI driver.
|
|
RHEL
|
OS used in Control Plane, Worker node and Admin Workstation
|
|
bmctl
|
bmctl is a command line tool for Google Distributed Cloud that simplifies cluster creation and management.
|
Procedure
Step 1: Create Google Distributed Cloud (software only) for bare metal previously known as Anthos clusters on bare metal. Download bmctl tool and install the cluster using it. Before running the cluster create command below, prepare the setup following the instructions in the Installation guide.
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]# bmctl create cluster --cluster=hv-anthos
[2025-12-09 04:43:30-0500] Runnning command: ./bmctl create cluster --cluster=hv-anthos
Please check the logs at bmctl-workspace/hv-anthos/log/create-cluster-20251209-044330/create-cluster.log
[2025-12-09 04:43:35-0500] Creating bootstrap cluster... OK
[2025-12-09 04:44:33-0500] Installing dependency components... ⠏
[2025-12-09 04:45:54-0500] Waiting for preflight check operator to show up... OK
[2025-12-09 04:46:24-0500] Waiting for preflight check job to finish... OK
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] - Validation Category: machines and network
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] - [PASSED] node-network
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.159-gcp
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.160
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.164-gcp
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.166
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] - [PASSED] pod-cidr
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.159
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.160-gcp
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.164
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.166-gcp
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] - [PASSED] gcp
[2025-12-09 04:49:44-0500] Flushing logs... OK
[2025-12-09 04:49:45-0500] Applying resources for new cluster
[2025-12-09 04:49:45-0500] Waiting for cluster kubeconfig to become ready OK
[2025-12-09 04:56:55-0500] Writing kubeconfig file
[2025-12-09 04:56:55-0500] kubeconfig of cluster being created is present at bmctl-workspace/hv-anthos/hv-anthos-kubeconfig
[2025-12-09 04:56:55-0500] Please restrict access to this file as it contains authentication credentials of your cluster.
[2025-12-09 04:56:55-0500] Waiting for cluster to become ready OK
[2025-12-09 05:05:05-0500] Please run
[2025-12-09 05:05:05-0500] kubectl --kubeconfig bmctl-workspace/hv-anthos/hv-anthos-kubeconfig get nodes
[2025-12-09 05:05:05-0500] to get cluster nodes status.
[2025-12-09 05:05:05-0500] Waiting for node pools to become ready OK
[2025-12-09 05:05:25-0500] Waiting for metrics to become ready in GCP OK
[2025-12-09 05:05:46-0500] Waiting for cluster API provider to install in the created admin cluster OK
[2025-12-09 05:05:56-0500] Moving admin cluster resources to the created admin cluster
[2025-12-09 05:05:59-0500] Flushing logs... OK
[2025-12-09 05:05:59-0500] Deleting bootstrap cluster... OK
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]#
After successful preflight checks and resource application, the cluster was ready with nodes running v1.31.13-gke.300.
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
cp164 Ready control-plane 18m v1.31.13-gke.300
worker159 Ready worker 12m v1.31.13-gke.300
worker160 Ready worker 12m v1.31.13-gke.300
worker166 Ready worker 13m v1.31.13-gke.300
Step 2: Install Hitachi CSI Plugin (HSPC) and Configure Storage. Refer HSPC Quick Reference Guide to install the driver. After installation, verify that HSPC is installed
[root@gdcv-admin operator]# kubectl get hspc -n kube-system
NAME READY AGE
hspc true 3m25s
Create a secret: Create a secret for the storage credentials. Provide base64 encoded storage username and password.
[root@gdcv-admin sample]# cat secret-e990.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: secret-e990
type: Opaque
data:
# base64 encoded storage url. E.g.: echo -n "http://172.16.1.1" | base64
url: aHR0cDovLzE3Mi4yMy42Ni4xNQ==
# base64 encoded storage username. E.g.: echo -n "User01" | base64
user: bWFpolRlbmFuY2U=
# base64 encoded storage password. E.g.: echo -n "Password01" | base64
password: cmFpZC1tYWludLLuYW5jZQ==
[root@gdcv-admin sample]# kubectl create -f secret-e990.yaml
secret/secret-e990 created
[root@gdcv-admin sample]# kubectl get secret
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
metrics-server-operator Opaque 0 36m
secret-e990 Opaque 3 7s
Create a storage class: To enable persistent storage for Cassandra, created a storage class. StorageClass file contains storage settings that are necessary for Storage Plug-in for Containers to work with your environment. Updated YAML file with StorageClass name, Storage serial number, HDP pool ID, Storage Port ID, connection type, filesystem type and secret name. The following sample provides information about the required parameters.
[root@gdcv-admin sample]# cat sc-e990.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: sc-e990
annotations:
kubernetes.io/description: Hitachi Storage Plug-in for Containers
provisioner: hspc.csi.hitachi.com
reclaimPolicy: Delete
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
allowVolumeExpansion: true
parameters:
serialNumber: "415855"
poolID: "3"
portID: CL5-A,CL6-A
connectionType: fc
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-publish-secret-name: "secret-e990"
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-publish-secret-namespace: "default"
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: "secret-e990"
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: "default"
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-publish-secret-name: "secret-e990"
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-publish-secret-namespace: "default"
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: "secret-e990"
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: "default"
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-name: "secret-e990"
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-namespace: "default"
[root@gdcv-admin sample]#
[root@gdcv-admin sample]# kubectl create -f sc-e990.yaml
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/sc-e990 created
[root@gdcv-admin sample]# kubectl get sc
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
anthos-system kubernetes.io/no-provisioner Delete WaitForFirstConsumer false 37m
local-disks kubernetes.io/no-provisioner Delete WaitForFirstConsumer false 37m
local-shared kubernetes.io/no-provisioner Delete WaitForFirstConsumer false 37m
sc-e990 hspc.csi.hitachi.com Delete Immediate true 11s
Step 3: Deploy Cassandra StatefulSet
We deployed a Cassandra StatefulSet with three replicas using Hitachi storage.
Service: Create a Headless service for StatefulSet. Open the URL cassandra-service.yml for the manifest file.

[root@gdcv-admin sample]# kubectl apply -f cassandra-service.yaml
service/cassandra created
[root@gdcv-admin sample]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
cassandra ClusterIP None <none> 9042/TCP 42m
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 21h
StatefulSet: Open the link cassandra-statefulset.yml for manifest file of Cassandra statefulset. The volume section is as follows. Provide the storageClass name and size of the volume.
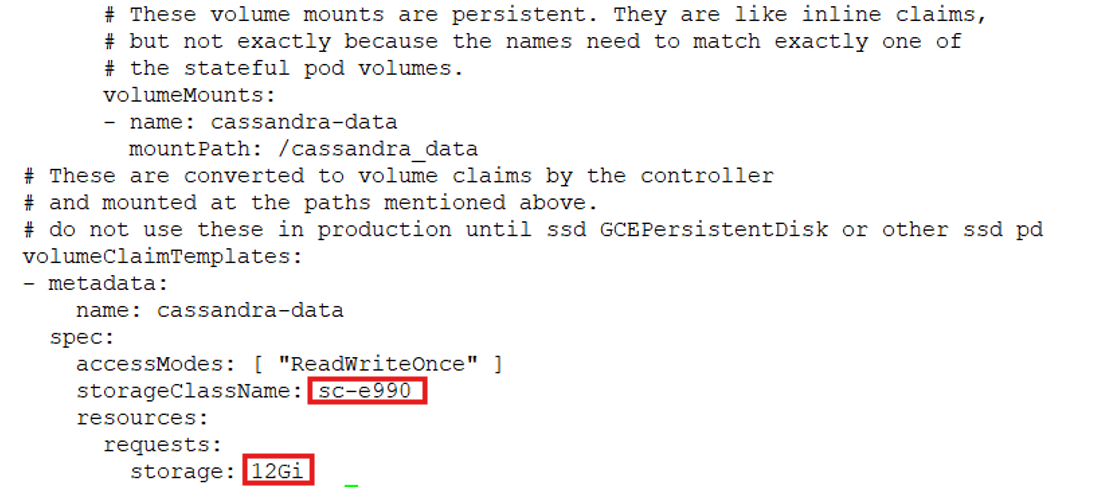
Run the following command to create the Cassandra StatefulSet
[root@gdcv-admin sample]# kubectl apply -f cassandra-statefulset.yaml
statefulset.apps/cassandra created
[root@gdcv-admin sample]#
Verify that the Cassandra nodes were healthy and replicated across the cluster.
[root@gdcv-admin sample]# kubectl get sts
NAME READY AGE
cassandra 3/3 51m
[root@gdcv-admin sample]#
[root@gdcv-admin sample]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cassandra-0 1/1 Running 0 8m35s
cassandra-1 1/1 Running 0 10m
cassandra-2 1/1 Running 0 11m
[root@gdcv-admin sample]kubectl exec -it cassandra-0 -- nodetool status
Datacenter: DC1-K8Demo
======================
Status=Up/Down
|/ State=Normal/Leaving/Joining/Moving
-- Address Load Tokens Owns (effective) Host ID Rack
UN 192.169.5.172 210.31 KiB 32 64.8% da9eb032-e726-419c-86d1-c95399b90d69 Rack1-K8Demo
UN 192.169.3.142 229.36 KiB 32 65.1% 70331a1e-ff02-4e54-96df-a07541da75c1 Rack1-K8Demo
UN 192.169.6.181 236.33 KiB 32 70.1% 5f599838-a957-46a6-b712-9d0bc7eeebda Rack1-K8Demo
[root@gdcv-admin sample]#
Verify that each pod mounted persistent volumes provisioned by the HSPC CSI driver.
[root@gdcv-admin sample]# kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS AGE
cassandra-data-cassandra-0 Bound pvc-d377fe31-d07f-4f4b-a26b-cbc660a6cefe 12Gi RWO sc-e990 <unset> 42m
cassandra-data-cassandra-1 Bound pvc-6a9079f5-669d-4770-84b5-8719e6e09746 12Gi RWO sc-e990 <unset> 41m
cassandra-data-cassandra-2 Bound pvc-78bffc07-6914-48b6-986e-f4efaae6d07c 12Gi RWO sc-e990 <unset> 40m
[root@gdcv-admin sample]#
Step 4: Upgrade Cluster from v1.31 to v1.32
Download the latest bmctl binary and initiate the upgrade:
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]# gcloud storage cp gs://anthos-baremetal-release/bmctl/1.32.700-gke.64/linux-amd64/bmctl .
Copying gs://anthos-baremetal-release/bmctl/1.32.700-gke.64/linux-amd64/bmctl to file://./bmctl
Completed files 1/1 | 129.3MiB/129.3MiB
Average throughput: 49.8MiB/s
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]# chmod +x bmctl
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]# bmctl version
bmctl version: 1.32.700-gke.64, git commit: 129fb6950142c813e047b5e1edc155dd3b7cc191, build date: 2025-11-22 12:27:40 PST , metadata image digest: sha256:24e91590349c5ad47df602196f16172e2dae1399826af479b326eceeda458900
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]#
Update anthosBareMetalVersion in the cluster configuration file.
[root@gdcv-admin hv-anthos]# cat hv-anthos.yaml |grep anthosBareMetalVersion
anthosBareMetalVersion: 1.32.700-gke.64
[root@gdcv-admin hv-anthos]#
Cluster version before upgrading.
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]# kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
cp164 Ready control-plane 21h v1.31.13-gke.300 172.23.57.164 <none> Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.4 (Plow) 5.14.0-427.13.1.el9_4.x86_64 containerd://1.7.28-gke.0
worker159 Ready worker 21h v1.31.13-gke.300 172.23.57.159 <none> Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.10 (Ootpa) 4.18.0-553.el8_10.x86_64 containerd://1.7.28-gke.0
worker160 Ready worker 21h v1.31.13-gke.300 172.23.57.160 <none> Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.4 (Plow) 5.14.0-427.13.1.el9_4.x86_64 containerd://1.7.28-gke.0
worker166 Ready worker 21h v1.31.13-gke.300 172.23.57.166 <none> Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.2 (Plow) 5.14.0-284.11.1.el9_2.x86_64 containerd://1.7.28-gke.0
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]#
Upgrade the cluster.
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]# bmctl upgrade cluster -c hv-anthos --kubeconfig /root/baremetal/bmctl-workspace/hv-anthos/hv-anthos-kubeconfig
[2025-12-10 03:01:21-0500] Running command: ./bmctl upgrade cluster -c hv-anthos --kubeconfig /root/baremetal/bmctl-workspace/hv-anthos/hv-anthos-kubeconfig
Please check the logs at bmctl-workspace/hv-anthos/log/upgrade-cluster-20251210-030121/upgrade-cluster.log
[2025-12-10 03:01:21-0500] Before upgrade, please use `bmctl backup cluster` to create a backup.
[2025-12-10 03:01:27-0500] "spec.gkeOnPremAPI" isn't specified in the configuration file of cluster "hv-anthos". This cluster will enroll automatically to GKE onprem API for easier management with gcloud, UI and terraform after upgrade if GKE Onprem API is enabled in Google Cloud services. To unenroll, set "spec.gkeOnPremAPI.enabled" to "false" after upgrade.
[2025-12-10 03:01:28-0500] The current version of cluster is 1.31.1100-gke.40
[2025-12-10 03:01:28-0500] The version to be upgraded to is 1.32.700-gke.64
[2025-12-10 03:01:28-0500] Waiting for preflight check operator to show up... OK
[2025-12-10 03:01:38-0500] Waiting for preflight check job to finish... OK
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - Validation Category: machines and network
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.164-gcp
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.166
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - [PASSED] gcp
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - [PASSED] node-network
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.159
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.166-gcp
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - [PASSED] cluster-upgrade-check
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - [PASSED] pod-cidr
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.159-gcp
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.160
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.160-gcp
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] - [PASSED] 172.23.57.164
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] Flushing logs... OK
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] Bumping the old version 1.31.1100-gke.40 to new version 1.32.700-gke.64 in the cluster resource.
[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] Waiting for machines to upgrade... pending: 4/4 upgraded: 0/4⠋ I1210 03:03:40.164895 1487306 request.go:697] Waited for 1.180098689s due to client-side throttling, not priority and fairness, request: GET:https://172.23.56.151:443/api/v1/namespaces/cluster-hv-anthos/pods/bm-system-machine-upgrade-preflight-chec67f2d98450a7c108518g2p5/log?container=a[2025-12-10 03:03:18-0500] Waiting for machines to upgrade... OK
[2025-12-10 03:25:09-0500] Writing kubeconfig file: clusterName = hv-anthos, path = bmctl-workspace/hv-anthos/hv-anthos-kubeconfig
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]#
The upgrade process validated machine and network checks, then rolled out the new version v1.32.9-gke.700 across all nodes.
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]# kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
cp164 Ready control-plane 22h v1.32.9-gke.700 172.23.57.164 <none> Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.4 (Plow) 5.14.0-427.13.1.el9_4.x86_64 containerd://1.7.29-gke.1
worker159 Ready worker 22h v1.32.9-gke.700 172.23.57.159 <none> Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.10 (Ootpa) 4.18.0-553.el8_10.x86_64 containerd://1.7.29-gke.1
worker160 Ready worker 22h v1.32.9-gke.700 172.23.57.160 <none> Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.4 (Plow) 5.14.0-427.13.1.el9_4.x86_64 containerd://1.7.29-gke.1
worker166 Ready worker 22h v1.32.9-gke.700 172.23.57.166 <none> Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.2 (Plow) 5.14.0-284.11.1.el9_2.x86_64 containerd://1.7.29-gke.1
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]#
Post-Upgrade Validation
After the upgrade, Cassandra pods remained stable:
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]# kubectl get sts
NAME READY AGE
cassandra 3/3 3h4m
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]#
Verify that persistent volumes were intact, and the cluster continued to serve workloads without disruption.
[root@gdcv-admin hv-anthos]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cassandra-0 1/1 Running 0 4m56s
cassandra-1 1/1 Running 0 86s
cassandra-2 1/1 Running 0 9m12s
[root@gdcv-admin hv-anthos]#
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]# kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS AGE
cassandra-data-cassandra-0 Bound pvc-d377fe31-d07f-4f4b-a26b-cbc660a6cefe 12Gi RWO sc-e990 <unset> 179m
cassandra-data-cassandra-1 Bound pvc-6a9079f5-669d-4770-84b5-8719e6e09746 12Gi RWO sc-e990 <unset> 178m
cassandra-data-cassandra-2 Bound pvc-78bffc07-6914-48b6-986e-f4efaae6d07c 12Gi RWO sc-e990 <unset> 177m
pvc-e990 Bound pvc-cfa6a148-60c5-4c05-9053-13f6a30297b9 1Gi RWO sc-e990 <unset> 22h
[root@gdcv-admin baremetal]#
Key Takeaways
Cluster Upgrade: Smooth transition from v1.31 to v1.32 using bmctl upgrade.
Hitachi CSI Integration: HSPC plugin v3.16.1 provided robust storage for stateful workloads.
Stateful Workload Resilience: StatefulSet remained healthy post-upgrade, validating the resilience of the setup.
Conclusion
This approach demonstrates how enterprise-grade storage and distributed databases can coexist in a modern hybrid cloud environment. By leveraging GDC (Software Only) on Bare Metal and Hitachi VSP storage, organizations can run stateful workloads with minimal downtime during upgrades.
Reference
· Upgrade GDC for bare metal cluster: https://docs.cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/distributed-cloud/bare-metal/docs/how-to/upgrade
· Quick Reference Guide on Hitachi Storage Plug-in for Containers Version 3.16.1: https://docs.hitachivantara.com/api/khub/documents/ue0_hsREFOjsI8_GLe065Q/content
#HybridCloudServices
#VSP5000Series