Introduction
In today’s fast paced IT landscape, virtualization is the backbone of modern data centers. Oracle Linux Virtualization Manager (OLVM) is Oracle’s enterprise class virtualization solution, built on the trusted KVM (Kernel based Virtual Machine) technology. It provides a powerful platform for managing virtual machines, networks, and storage with ease. By integrating Hitachi VSP One Block storage with OLVM, organizations gain a powerful, high-performance, and low-latency platform. Hitachi VSP’s enterprise-grade flash and NVMe architecture accelerates VM operations and delivers faster application response times
This blog will walk through OLVM’s integration and use cases, helping you understand how to leverage it for building a robust virtualization environment.
Key Component of OLVM cluster
· · Engine: The central management server that provides a web-based interface for administrators to control the virtualization environment.
· Host: A physical server running Oracle Linux with KVM enabled. Hosts provide compute resources for VMs.
· Cluster: A logical grouping of hosts within a data center. Clusters define policies such as CPU type compatibility and scheduling.
· Data Center: The highest-level container in OLVM. It groups clusters, storage domains, and networks together for centralized management.
· Storage Domain: A storage repository (NFS, iSCSI, Fibre Channel, or GlusterFS) where VM disks, ISO images, and snapshots are stored. Hitachi VSP Storage integration with OLVM Storage Domain will be explained in the Blog.
· Virtual Machine (VM): A guest operating system instance running on a host. VMs are managed through the Engine and can be migrated between hosts.
· Network: Logical networks defined within OLVM that connect VMs and hosts. These can be bridged to physical NICs for external connectivity.
· High Availability (HA): A feature ensuring that critical VMs automatically restart on another host if the original host fails.
· VirtIO Drivers: Para virtualized drivers that improve performance of disk and network I/O for VMs.
Configuration details
Engine host: The Engine host is responsible for managing the KVM hosts. It runs Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8.10 and has Oracle Linux Virtualization Manager (OLVM) version 4.4.10.7-1.0.25.el8 installed.
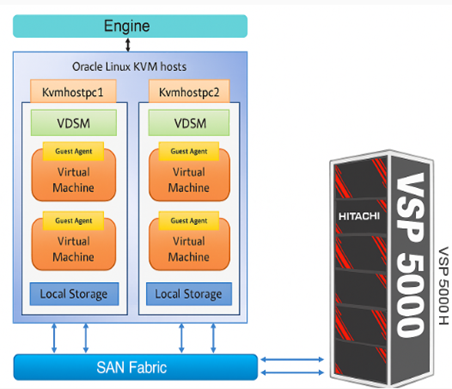
KVM Hosts: The environment includes two KVM hosts (kvmhostpc1 and kvmhostpc2). Both hosts are connected to Hitachi VSP 5600H storage through fabric switches. Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8.6 and 8.10 were installed on KVM host respectively.
Hitachi VSP 5600H Storage: Two 32 Gbps FC ports were used to provide block storage volume to the OLVM KVM hosts.
The following diagram shows OLVM configuration environment
Storage provisioning and multipathing
A total of 10 LUNs were provisioned from the Hitachi VSP 5600H storage system and presented to both KVM hosts. Each host has access to the same set of shared LUNs.
Note: If a file system of 10GB needs to be created, then 15GB LUN should be provisioned from storage because OLVM itself consumes almost 5GB of space for metadata.
Device Mapper Multipath was configured on both KVM hosts to provide multipath I/O management and redundancy. As a part of this configuration, a custom multipath configuration file named hitachi.conf (the filename is arbitrary) was created under the directory: /etc/multipath/conf.d/
The file was populated with the required vendor‑specific parameters for Hitachi storage, as shown below:
[root@kvmhostpc1 conf.d]# cat hitachi.conf
devices {
device {
vendor "(HITACHI|HP)"
product "OPEN-.*"
path_grouping_policy "multibus"
no_path_retry 10
features "0"
hardware_handler "0"
path_checker "tur"
prio "const"
rr_weight "uniform"
}
}
[root@kvmhostpc1 conf.d]#
After completing the configuration, the multipath -ll command confirms that the same LUNs are visible and active on both KVM hosts.
[root@kvmhostpc1 ~]# multipath -ll
360060e80087538000050753800000115 dm-9 HITACHI ,OPEN-V
size=16G features='1 queue_if_no_path' hwhandler='0' wp=rw
`-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=1 status=active
|- 1:0:0:6 sdi 8:128 active ready running
`- 3:0:0:6 sdv 65:80 active ready running
360060e8008753800005075380000010c dm-2 HITACHI ,OPEN-V
size=100G features='1 queue_if_no_path' hwhandler='0' wp=rw
`-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=1 status=active
|- 1:0:0:10 sdm 8:192 active ready running
`- 3:0:0:10 sdz 65:144 active ready running
[root@kvmhostpc2 conf.d]# multipath -ll
360060e80087538000050753800000115 dm-9 HITACHI,OPEN-V
size=16G features='1 queue_if_no_path' hwhandler='0' wp=rw
`-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=1 status=active
|- 2:0:0:6 sdq 65:0 active ready running
`- 5:0:0:6 sdo 8:224 active ready running
360060e8008753800005075380000010c dm-2 HITACHI,OPEN-V
size=100G features='1 queue_if_no_path' hwhandler='0' wp=rw
`-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=1 status=active
|- 2:0:0:10 sdy 65:128 active ready running
`- 5:0:0:10 sdv 65:80 active ready running
OLVM Cluster configuration
Install OLVM packages in the Engine host and configure them using ‘engine-setup’ command. It will generate the following URL. Access this URL to configure kvmhosts and cluster.
https://olvmclusterpc.lab.com:443/ovirt-engine
To login to this URL, use the user 'admin@internal' and the password specified while executing the ‘engine-setup’ command.
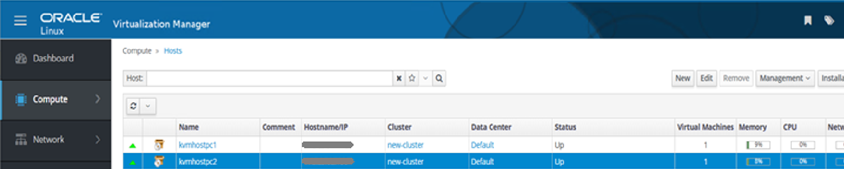
A. Login to the administrative console, click on Compute, then Hosts, click on new button and add the KVM hosts. For detailed steps, refer to the Oracle Linux Virtualization Manager Guides.
B. To configure High Availability, go to Compute, then Cluster and click on Migration Policy. Set Migration policy of cluster to ‘Minimal downtime’. Migration policies in OLVM allow administrators to define how VMs are prioritized and handled during live migrations or host failures. Set Resilience policy to ‘Migrate Virtual Machines’. A resilient policy ensures HA by automatically restarting failed VMs on healthy hosts.
The fencing policy defines how the cluster isolates and manages unresponsive hosts to protect data integrity and ensure HA of VMs.
To set fencing policy, enable following three parameters:
· Enable fencing
· Skip fencing if host has live lease in storage
· Skip fencing on cluster connectivity issues
C. Storage LUNs provisioned through Hitachi VSP 5600H are visible in host devices tab under hosts tab. These LUNs are used to create storage domains, and these storage domains are used to create VMs and file systems. The procedure for creating storage domains using these LUNs is demonstrated later in this blog.
D. Enable HA in KVM hosts and VMs.
· Configure Power Management in the KVM hosts. Navigate Compute, then Hosts, click on the host needs to be modified, then click on edit tab and configure the fencing agent.
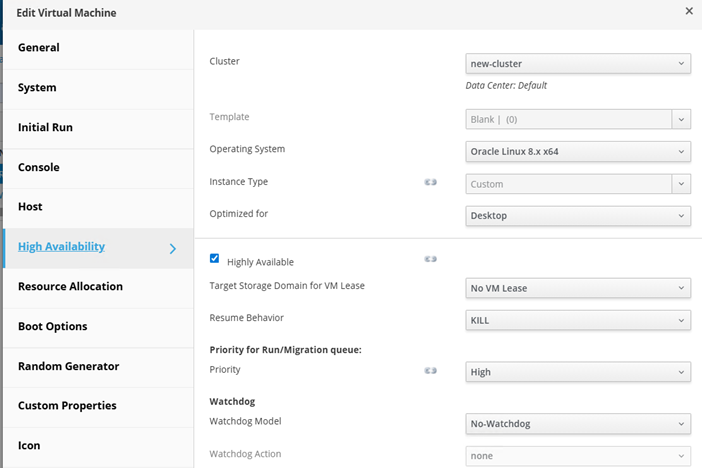
· Enable HA on the VMs. Navigate Compute, then Virtual Machines, click on edit and then configure High availability and Resource allocation. The following screenshots demonstrate options required to be configured.
As shown in the following screenshot, configure High availability.
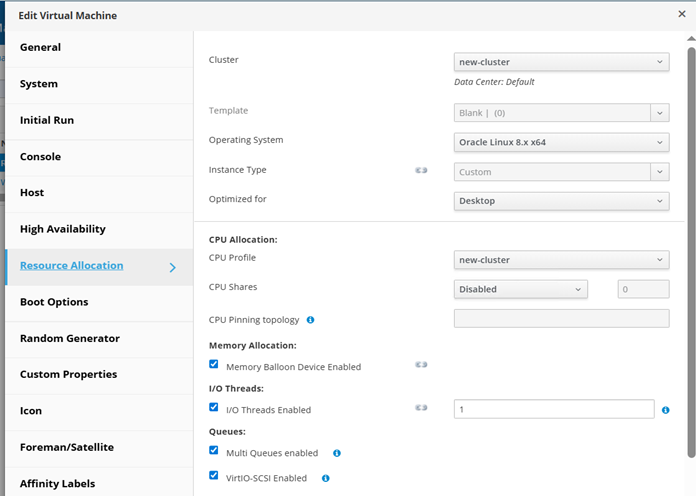
As shown in the following screenshot, configure Resource allocation.
Configuring OLVM storage domain with Hitachi VSP 5600H storage
The following screenshots show how to create a storage domain and assign the same to VMs.
1. In the Administrative console, navigate to Storage, click on Domains, then click New Domain tab. In the New Domain menu, input data as shown in the screenshot and select the Hitachi VSP LUN to use for creating the domain. Click on OK.
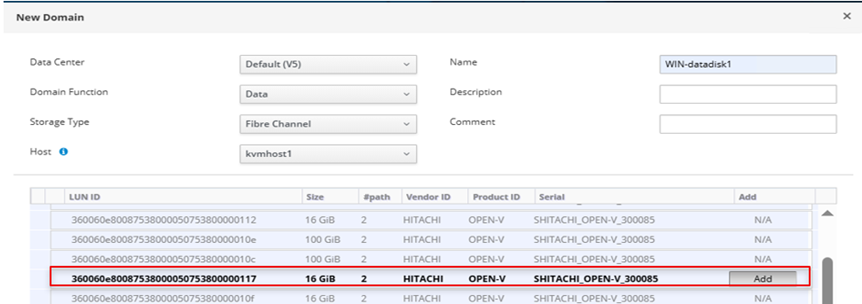
2. The following screenshot shows that the storage domain WIN-datadisk1 has been successfully created.
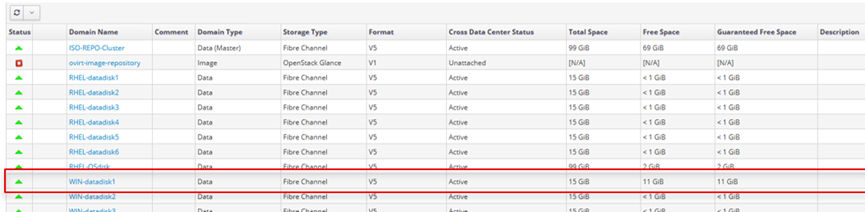
3. Assign the newly created storage domain to VM using the procedure demonstrated below.
In the administrative console, select the VM where the storage LUN needs to be added and click on edit tab.
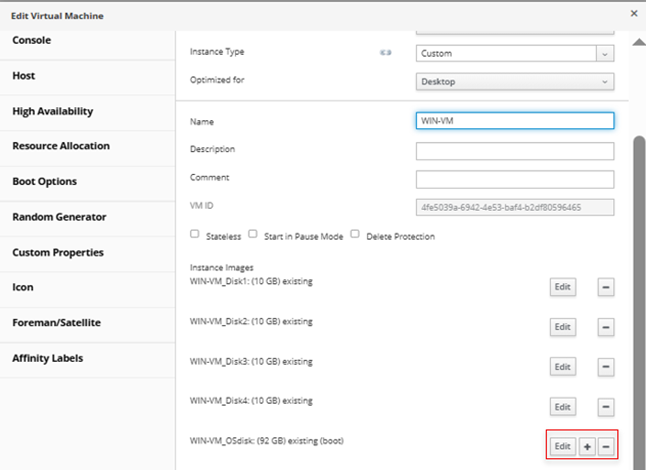
In the Edit Virtual Machine menu, click on + sign and then click “Create” and it will open the following window. Fill up the fields as needed and click on “OK”.
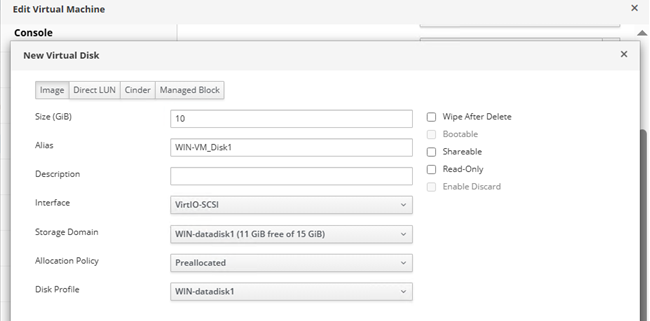
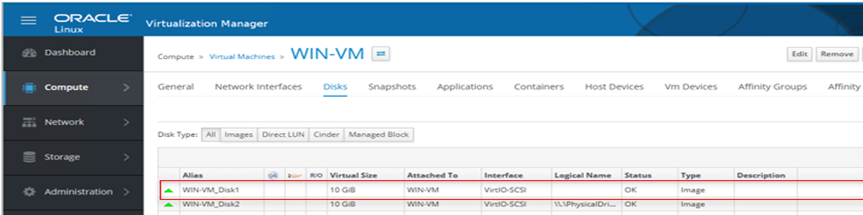
From the excerpt below, it is seen that WIN-datadisk1 storage domain has been assigned to VM “WIN-VM” as WIN-VM_Disk1.
Migration of VMs
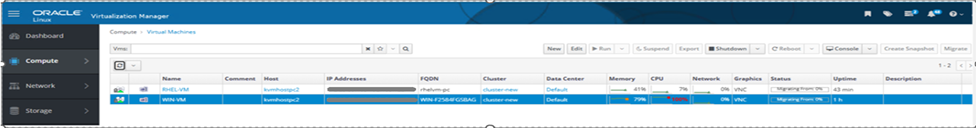
VM migration means moving a virtual machine from one physical server to another. It helps with load balancing, hardware maintenance, disaster recovery, and better use of resources. VM migration is an important feature of virtualization that improves flexibility, reliability, and uptime. From the screenshot below, it can be seen that the VMs are running on kvmhostpc2.
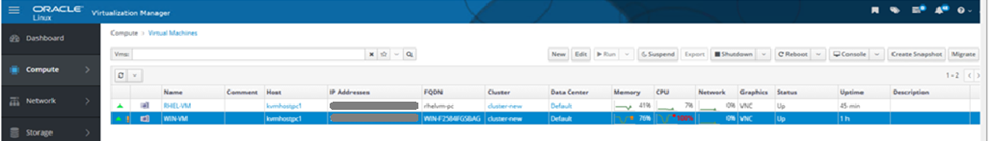
To start the migration, select the VM to be migrated, right click on the VM and select migrate option. As shown in the screenshot below, the migration has been completed successfully. The VMs have been moved from kvmhostpc2 to kvmhostpc1.
Use cases of OLVM with Hitachi VSP 5600H storage.·
· Data Center Consolidation: OLVM allows enterprises to run multiple workloads on fewer physical servers, reducing hardware costs and improving energy efficiency.
· High-Availability Clusters: With built-in clustering and failover, OLVM ensures critical applications remain available even if a host fails.
· Disaster Recovery: Snapshots, live migration, and replication features help organizations quickly recover workloads in case of system failures.
· Test and Development Environments: Developers can spin up isolated VMs rapidly, test software across different OS versions, and roll back changes easily.
Conclusion
Configuring OLVM with Hitachi VSP 5600H is not just about setting up a hypervisor; it’s a strategic move toward efficiency, scalability, and security. By consolidating workloads, streamlining management, and leveraging enterprise-grade virtualization, organizations can reduce complexity while gaining flexibility to adapt to future demands.
#VSP5000Series