Resilient Infrastructure with VCF 9: Stretched Cluster Using Hitachi VSP and Global Active Device (GAD)
Introduction
In today’s always-on digital landscape, enterprise IT teams are under pressure to deliver high availability, seamless scalability, and operational efficiency. VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 9.0 rises to the occasion with native support for Fibre Channel (FC)-based VMFS storage using Hitachi VSP and stretched cluster capabilities. When paired with Hitachi Global-Active Device (GAD) replication, organizations gain a resilient, enterprise-grade solution for mission-critical workloads across geographically separated sites.
Infrastructure Architecture Overview
The stretched cluster design integrates VCF’s SDDC management with Hitachi GAD’s active-active replication:
1. Sites: Two active sites (Site 1 hosting the Management Domain, Site 2 hosting the VI Workload Domain).
2. vSphere Layer: A single vSphere stretched cluster spans both sites, sharing a mounted datastore. If one site fails, VMs restart automatically on the other (HA restart).
3. Storage Layer: Hitachi GAD synchronously mirrors data between VSP arrays (e.g., VSP One, 5600H and 5500H).
4. Quorum: A Quorum Disk (e.g., VSP One, E1090) acts as a tie-breaker to prevent split-brain scenarios.
This architecture ensures continuous service availability across two data centers by combining VCF’s automation with Hitachi’s synchronous replication.
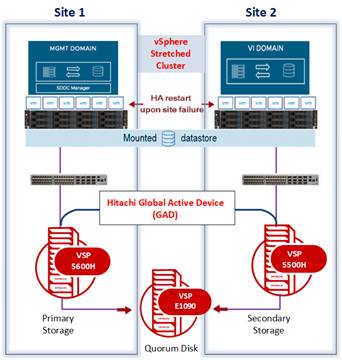
Image: VCF Stretched Cluster with Fibre Channel-Based Storage and Hitachi Global-Active Device Integration
Why VCF 9 + Hitachi GAD?
VCF 9 introduces:
- Native support for FC-based VMFS storage in the management domain
- Enhanced SDDC Manager with granular lifecycle control, including VCF Operations Role (noting that SDDC Manager will be degraded from VCF 9.1).
- Stretched cluster support for zero RTO failover
- Seamless integration with Hitachi GAD for active-active synchronous replication
Together, these features deliver a robust, enterprise-grade solution for mission-critical workloads across geographically separated sites.
Configuration Steps
Storage Configuration: Hitachi GAD Integration
Before deploying VCF, you’ll need to configure your Hitachi storage systems for GAD:
1. Reserve LDEV IDs: Ensure consistent volume mapping across sites.
2. Create LUN Paths: Zoning and masking ensure secure, multipath access from ESXi hosts to storage.
3. Configure Quorum Disk: Use a shared volume for arbitration between arrays.
4. Establish Remote Paths: Enable bidirectional connectivity for replication.
5. Create GAD Pairs: Set up synchronous replication between primary and secondary volumes.
6. Present GAD Volumes: Expose replicated volumes to ESXi hosts with multipathing.
Deploying the Stretched Management Domain
The management domain is the backbone of VCF. Stretching it across sites ensures that core services (vCenter, NSX, SDDC Manager) remain available even during site outages. VCF 9.0 simplifies the deployment of a stretched management domain using FC-based VMFS storage:
· Fleet Deployment: VCF uses a fleet model to deploy multiple components in a coordinated fashion.
· VCF Installer Flexibility: The VCF Installer can reside on any compatible host, allowing for resource isolation.
· FC-Based Storage Selection: Choosing FC over vSAN enables integration with Hitachi VSP arrays.
Prerequisites
- 2–4 ESXi 9.0 hosts (minimum 2 per site)
- Storage Arrays: Supported Hitachi VSP systems with GAD license enabled.
- Pre-zoned FC SAN with VMFS datastores
- DNS, NTP and IP reservations
- Downloaded VCF 9.0 bundles
Deployment Highlights
- Deploy the VCF Installer OVA on a primary site host.
- Choose between “High Availability” or “Simple” deployment models.
- Select FC-based external storage and specify the GAD-backed datastore.
- Complete network, host, and appliance configurations.
- Validate and deploy via the VCF Installer UI.
Note: The VCF Installer can reside on the same or a different host than the SDDC Manager VM, offering flexibility for lab or production environments.
Adding a Stretched VI Workload Domain
Once the management domain is live, you can deploy a stretched VI Workload Domain:
- Commission Hosts: Ensure FC zoning and GAD replication are in place.
- Create the Domain: Use VCF Operations to configure vCenter, NSX, and storage.
- Verify: Confirm both domains appear in SDDC Manager.
Managing Stretched Datastores
To Add stretched datastore:
· Present new GAD-backed LUNs to all ESXi hosts.
· Mount and format the datastore in vCenter.
· Apply storage policies and validate in VCF inventory.
To Remove stretched datastore:
· Migrate or power off VMs.
· Unmount and detach the datastore.
· Clean up SPBM policies and FC zoning.
Validation and Monitoring
After deployment, perform controlled failover/failback tests to validate resilience:
· Storage: Ensure surviving site promotes storage, paths fail over cleanly, and replication remains healthy.
· Compute: Verify HA restarts VMs without delay or orphaned states.
· Networking: Confirm NSX overlays and Edge nodes fail over correctly.
· Management: Validate vCenter, NSX Manager, and SDDC Manager remain available.
· Failback: Restore FC fabrics, re-sync replication, and confirm full path redundancy.
Monitoring should include:
· vSphere HA/DRS events
· Storage multipathing states (active/optimized vs non-optimized)
· NSX health monitoring
· VCF service alarms and logs
Benefits
· Zero RTO Failover: VMs restart seamlessly across sites.
· Enterprise-Grade Resilience: Active-active synchronous replication with Hitachi GAD.
· Operational Efficiency: Automated lifecycle management via VCF.
· Flexibility: Native FC-based VMFS support in both management and workload domains.
· Future-Proof: Scalable architecture for hybrid cloud and edge deployments.
Conclusion
VCF 9.0 with Hitachi VSP and Global Active Device (GAD) provides a robust blueprint for building resilient, scalable, and high‑performing hybrid cloud environments. By combining VCF’s automation and lifecycle management with Hitachi VSP’s enterprise storage capabilities and synchronous replication through GAD, enterprises can modernize their data centers while ensuring continuous availability across sites. This integrated solution delivers the tools, flexibility, and confidence required to support mission‑critical workloads and to future‑proof infrastructure for both hybrid cloud and edge use cases.
You can find additional information at the Link
#VSPOneBlock#GlobalActiveDevice