Introduction
As enterprises modernize their IT infrastructure, the demand for flexible, automated, and resilient storage solutions continues to grow. This blog explores how combining Red Hat Ansible with Hitachi Vantara VSP One Block Storage simplifies the deployment of iSCSI Global-Active Device (GAD) pairs, delivering agility, reliability, and operational efficiency for mission-critical environments. By leveraging iSCSI connectivity, organizations can achieve high availability and business continuity without the complexity of traditional SAN configurations.
Why Use Ansible to Automate iSCSI GAD Configuration?
iSCSI GAD enables active-active, synchronous mirroring of volumes between two Hitachi Vantara storage systems over Ethernet, ensuring seamless failover and uninterrupted host access.
Manually setting up iSCSI GAD can be complex, slow, and prone to error, especially in large enterprise environments with multiple hosts, storage arrays, and network paths.
Ansible solves these challenges with its agentless, open-source automation framework and simple, human-readable YAML playbooks. By combining Ansible with Hitachi Vantara VSP One Block Storage, organizations gain:
- Configuration Consistency: Ensure uniform settings across all storage systems
- Deployment Repeatability: Automate even the most intricate iSCSI GAD setups
- Operational Speed and Efficiency: Reduce manual effort and accelerate provisioning
This approach empowers IT teams to streamline storage operations, minimize misconfigurations, and fully leverage the reliability, high availability, and advanced capabilities of Hitachi Vantara storage.
Infrastructure Architecture Overview
The diagram below illustrates the test environment used for validation, where the Ansible Control Node is directly connected to the Hitachi VSP One series storage system.
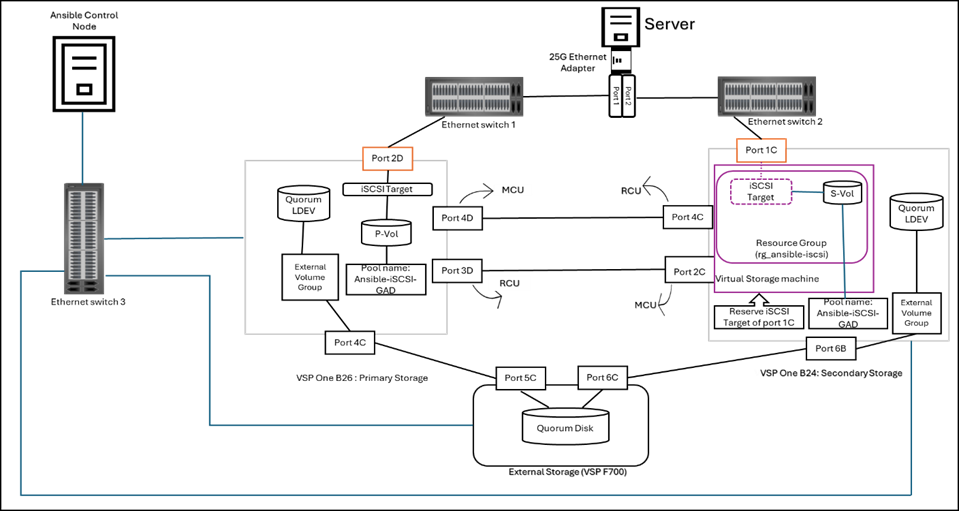
Resources used in this environment:
- Primary storage: Hitachi VSP One B26 (SVOS 10.4.1- A3-04-21-40/00) used for primary site storage system.
- Secondary storage: Hitachi VSP One B24 (SVOS 10.4.1- A3-04-21-40/00) used for secondary site storage system.
- External storage system: Hitachi VSP F700(SVOS 9.6.0 - 88-08-14-60/00) used for External site storage system.
- Ethernet Switches: One Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2(fw: v10.5(2)) & one Cisco Nexus 93180YC-FX3(fw: v10.5(2)) used for iSCSI host connectivity.
One Cisco nexus switch to provide Management network connectivity between resources.
- Ansible Control Node: RHEL 8.10 with Red Hat Ansible Core version 2.16.3 & Python version 3.12.1 is used as the Ansible control node for storage provisioning.
- Test Server: ESXi 8.0 U3 is used as a test server.
Installation package of Hitachi Vantara Storage Modules for Red Hat Ansible
- To install the latest version of the Hitachi storage modules from GitHub and use it, run the following command on the Ansible control node using the Ansible Galaxy CLI:
ansible-galaxy collection install hitachivantara.vspone_block
- You can also install a specific version with the following command:
ansible-galaxy collection install hitachivantara.vspone_block:==4.5.0
- To update the collection to the latest version, execute the following command:
ansible-galaxy collection install hitachivantara.vspone_block –upgrade
- After installation, the sample playbooks for Hitachi Vantara VSP storages will be available in the following path:
/root/.ansible/collections/ansible_collections/hitachivantara/vspone_block/playbooks/vsp_direct
User can modify or create new playbooks according to their need.
iSCSI GAD Pair Configuration: Playbooks Overview
Once the installation is complete, the Ansible playbooks were customized to meet the specific needs of the test environment. These customized playbooks were then run to automate the setup of iSCSI GAD pairs, enabling consistent, efficient, and reliable deployment of active-active volume replication across the connected Hitachi VSP One storage systems.
The configuration was carried out by performing the following tasks using the playbooks listed below:
- Get DP Pool & Parity Group:
Collect facts about DP pool details and retrieve parity group information to verify health and capacity before creating DP pools on both primary and secondary storage systems using get_pool_paritygrp_info.yml.
- Get free LDEV ID’s:
Check free LDEV IDs on both the primary and secondary storage system to be used for GAD pairing using get_free_ldevid_pri_sec.yml.
- DP Pool & DRS volume Creation in Primary Storage:
Provision DP Pools and create DRS volume(P-Vol) on Primary storage systems create_pool_DRSvol_pri.yml.
- Get Storage Port Info:
Gather storage port details for both Primary and Secondary Storages via port ID using get_port_info.yml.
- Configure iSCSI Port:
Configure the iSCSI port with the required parameters using configure_iscsi_port.yml.
Note: This playbook can be used to configure all iSCSI ports required for host connections or remote connections.
- Create iSCSI Target with volume and Update Host Mode (Primary Storage)
Create a new iSCSI target by adding the host IQN, attaching the DRS volume (primary storage only), and updating the Host Mode and HMO(Host Mode Option) using create_iscsitarget_addvol_update_HM_HMO_pri.yml.
- DP pool Creation in Secondary storage :
Create a DP pool only on the Secondary Storage system using create_pool_sec.yml.
- Create iSCSI Target and Update Host Mode (Secondary Storage)
Create a new iSCSI target by adding only the host IQN, without attaching any secondary volume, and update the Host Mode and Host Mode Option (HMO) using create_iscsitarget_update_HM_HMO_sec.yml.
Note: The secondary volume will be automatically created from this DP pool during GAD pair creation.
- Create Resource Group & Reserve iSCSI Target (Secondary Storage):
Create a resource group on the secondary storage using the primary storage serial number and model as virtual identifiers, and reserve the iSCSI target for host connection using create_rg_with_iscsi_target.yml.
- Register Remote storage:
Before creating a remote connection, the remote storage must be registered using register_remote_storage.yml.
- Create iSCSI Remote Connection:
Establish bidirectional remote connections between the primary and secondary storage systems. This activity is completed in two steps: first, registering the iSCSI ports, and then adding the remote paths. The playbook used for this activity is iscsi_remote_connection.yml, and it can be used for both primary and secondary storage systems.
- Create Volume, Host Group & Add Volume to Host Group on External Storage:
Create an LDEV (as an external volume), then create a host group on the external storage port connected to the primary and secondary storage systems and map the LDEV with the WWNs of the primary and secondary storage ports.
Playbook used: create_ldev_hostgrp_ext.yml
Note: External storage connectivity is configured using FC. iSCSI connectivity to external storage from VSP Block 20 series is supported only when the external storage is also VSP Block 20. Since only two units in our environment support iSCSI connectivity, FC is used for the external storage connection.
- External Volume Addition & Quorum Disk Registration:
Add virtual external volumes using the external storage LDEV IDs as quorum disks on both systems.
Playbooks used: external_vol_add.yml and quorum_disk_registration.yml
Note: An external volume with external path should already be presented in the local storage (primary storage and secondary storage) in advance to provision new external volumes using the playbooks, as this is currently out of scope.
- Create iSCSI GAD Pair:
Create an iSCSI GAD pair between the Storage system.
Playbook used: gad_pair_iscsi.yml.
The complete set of playbooks for this setup is available at the following URL:
iSCSI-GAD-VSPOneB20
How to Run and Troubleshoot Ansible Playbooks
- Before executing any playbook tasks, the user must manually input the storage credential variables into the ansible_vault_storage_var.yml file located at the following path:
/root/.ansible/collections/ansible_collections/hitachivantara/vspone_block/playbooks/ansible_vault_vars
- Execute a playbook task using this command syntax:
ansible-playbook <name of the yml file>
- To get detailed output, run the playbook with verbose mode using the following syntax:
ansible-playbook <name of the yml file> -vvv
- To troubleshoot issues, refer to the log file located at:
$HOME/logs/hitachivantara/ansible/vspone_block/hv_vspone_block_modules.log
$HOME/logs/hitachivantara/ansible/vspone_block/hv_vspone_block_audit.log
Conclusion
Integrating Red Hat Ansible with Hitachi Vantara VSP One Block Storage simplifies and accelerates the deployment of iSCSI Global-Active Device (GAD) pairs. Automation reduces configuration complexity while ensuring high availability and consistent active-active storage behavior for business-critical workloads.
By adopting Ansible-driven automation for iSCSI GAD, organizations can build resilient, scalable, and easy-to-manage storage environments that are well aligned with modern infrastructure demands.
References
The following URLs provide additional information and resources:
Public repository for Hitachi Storage Modules for Red Hat® Ansible®
Ansible playbooks - Ansible Community Documentation
Ansible Galaxy
#VSPOneBlock