Introduction
This blog provides insights into the compatibility of the Hitachi Virtual Storage Platform One Block 20 (VSP One Block 20) midrange storage systems with AWS EC2 instances running Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 9.4.
The primary focus area of this blog is It also offers the users step-by-step instructions on configuring the NVMe/TCP I/O timeout settings on RHEL 9.4 AWS EC2 instance to mitigate potential I/O process hang issues arising from storage hardware failures.
What is I/O Process hang issue?
An I/O process hang issue occurs when a process in a Linux system enters the uninterruptible sleep state, commonly referred to as the 'D' state. In this state, the process is waiting for an I/O operation to complete, such as reading from or writing to a disk, network socket, or other hardware device. The 'D' state indicates that the process is in uninterruptible sleep, meaning it cannot be woken up or terminated until the I/O operation finishes.
Environment
NVMe/TCP (100Gb) configuration is tested with the following components:
- AWS EC2 Instance with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.4 (Type: c6in.16xlarge to support 100G network performance)
- Cisco Nexus 93180YC-FX
- VSP One Block 20 family mid-range storage system
- CCI host with OS RHEL 8.6 and Command Control Interface version 01-76-03/02
Configuration Layout
The following figure shows the hybrid cloud environment with Hitachi VSP One Block 28 and AWS EC2 running RHEL 9.4 with NVMe/TCP configuration over 100G Direct Connect:
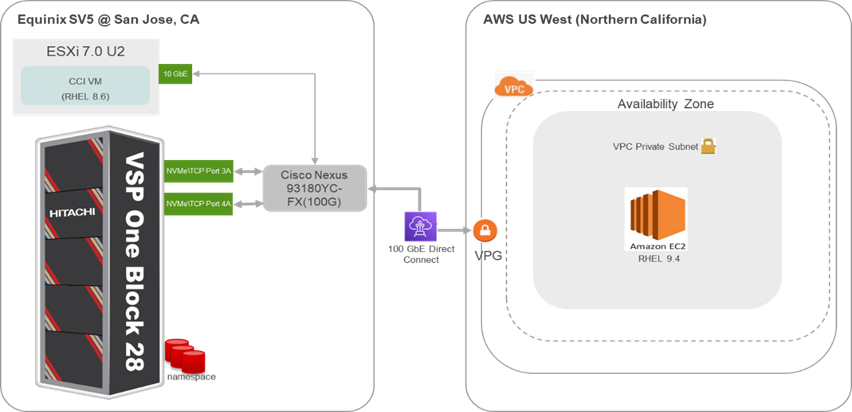
- Hybrid cloud environment
A hybrid cloud environment combines on-premises infrastructure with public and private cloud services, enabling seamless data and application sharing across platforms for enhanced flexibility and scalability.
- Hitachi VSP One Block 28
The Hitachi Virtual Storage Platform (VSP) One Block 28 is a midrange all-flash storage system designed for enterprise workloads.
- RHEL 9.4 (AWS EC2)
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) provides scalable computing capacity in the cloud. Running Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 9.4 on EC2 instances offers a secure and stable platform for applications.
- NVMe/TCP
It is a storage protocol that enables high-speed, low-latency access to NVMe devices over standard Ethernet networks using the TCP/IP stack. This approach allows organizations to leverage existing network infrastructure without the need for specialized hardware like Fibre Channel or RDMA adapters, making it a cost-effective solution for high-performance storage needs.
- 100G Direct Connect
AWS Direct Connect is a cloud service that establishes a dedicated, private connection between your on-premises infrastructure and AWS. Utilizing 100G Direct Connect provides high bandwidth and low latency, essential for data-intensive applications and real-time data processing.
Issue Observed
The following error was found in RHEL 9.4 AWS EC2 during VSP One B20 Storage hardware component failure event for NVMe/TCP (100Gb) configuration:
Some of the I/O processes on the disks are going into a 'D' state and are not resuming.
task seqtp29c_64:2618 blocked for more than 245 seconds
Not tainted 5.14.0-362.18.1.el9_3.x86_64 #1
"echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/hung_task_timeout_secs" disables this message.
task:seqtp29c_64 state:D stack:0 pid:2618 ppid:1 flags:0x00000002
Cause of the Issue
For AWS EC2 instance with Red Hat Linux 9.4 version (ami-0c5ebd68eb61ff68d), the default I/O timeout for NVMe devices is set to ‘4294967295’ seconds. Due to this I/O processes get suspended for some storage failure scenarios.
Resolution
Depending on the Linux version, the default value of nvme_core.io_timeout parameter might already be set at the maximum allowed value. On an AWS EC2 instance with RHEL 9.4 (ami-0c5ebd68eb61ff68d), the default value is 4294967295, which is unusually high.
You can verify the default I/O time out value for the RHEL host with the following command:
#cat /sys/module/nvme_core/parameters/io_timeout
4294967295
For uninterrupted operation in the event of a storage hardware failure, you must configure the NVMe core I/O timeout value to a low value (for example, ‘60’ seconds as per VSP guidelines) with the following command and reboot the system so settings should take effect to both existing and future NVMe devices.
Syntax
# grubby --args=nvme_core.io_timeout=<I/O timeout value> --update-kernel /boot/<vmlinuz-file>
Example
#grubby --args=nvme_core.io_timeout=60 --update-kernel /boot/ vmlinuz-5.14.0- 427.20.1.el9_4.x86_64
For more details, see the following link:
Configuring NVMe TCP with AWS EC2 Instance Running RHEL on VSP One Block 20 NVM Subsystems
Conclusion
By configuring NVMe/TCP I/O timeout settings appropriately, organizations can effectively mitigate potential I/O hang issues arising from storage Hardware failures.